Chrome Concentrate

Exporting chrome concentrate from Zimbabwe involves a series of regulatory, logistical, and business processes that ensure compliance with local laws and international trade standards. Here's an overview:
1. Mining and Production
- Licensing and Compliance: Before mining chrome, companies must obtain a mining license from Zimbabwe's Ministry of Mines and Mining Development. This process includes securing prospecting rights, carrying out exploration, and applying for a mining permit.
- Extraction and Concentration: Chrome ore is extracted from underground or open-pit mines. The ore is then processed to increase the chromium content, creating chrome concentrate, which is the export product.
2. Regulatory Compliance
- Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA): Companies must conduct an EIA before starting mining operations. This assessment evaluates the environmental impact of the mining activities, and the Environmental Management Agency (EMA) must approve it before operations can begin.
- Mining Taxes and Royalties: Companies are required to pay royalties on the chrome they produce, which is a percentage of the gross revenue. Additionally, there are mining taxes and fees that must be paid to the government.
- Export Permits: Before exporting chrome concentrate, companies must obtain an export permit from the Ministry of Mines and Mining Development. The permit ensures that the export is legal and that the correct royalties and taxes have been paid.
3. Processing and Value Addition
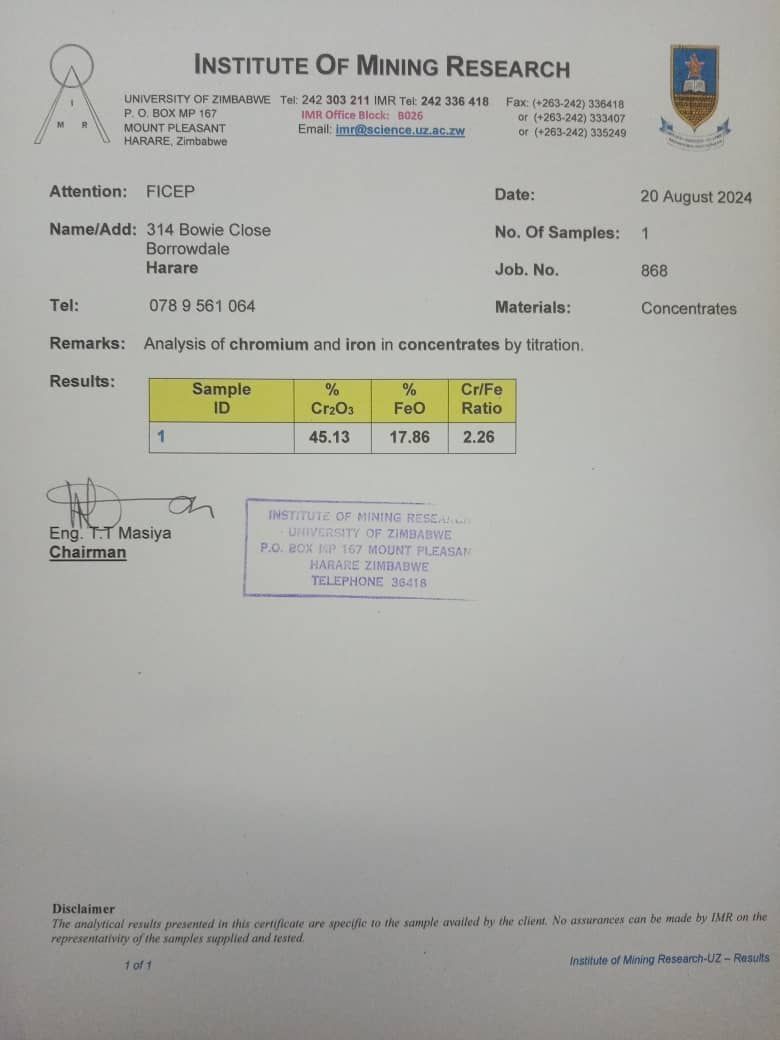
- Concentration Plants: To meet export standards, chrome ore is processed in concentration plants, where it is crushed and separated to increase the chrome content. The final product is chrome concentrate, which typically has a higher chromium-to-iron ratio.
- Value Addition Policies: The Zimbabwean government has been encouraging the local processing of chrome into ferrochrome (an alloy of chromium and iron) before export. This is part of a broader policy to add value to mineral exports and create jobs within the country.
4. Logistics and Transportation
- Transport Infrastructure: Chrome concentrate is transported by road or rail to ports for export. Common routes include transport to South African ports such as Durban, which is a key exit point for Zimbabwe’s mineral exports.
- Customs and Border Control: At the border, the export must pass through customs, where documents are verified, and duties or other fees are paid. Proper documentation is crucial for a smooth export process.


Trade Policies and Support
- Government Support: The South African government provides various forms of support to the macadamia nut industry, including research and development funding, export incentives, and assistance with market access.
- Trade Agreements: South Africa benefits from trade agreements that facilitate easier access to international markets. These agreements help reduce tariffs and other barriers, making South African macadamia nuts more competitive globally.
5. Export Markets
- Key Markets: Zimbabwe exports chrome concentrate primarily to China, which is the largest global consumer of chrome, used in the production of stainless steel. Other markets include India and parts of Europe.
- Global Demand: The demand for chrome is closely linked to the steel industry. As global steel production fluctuates, so does the demand for chrome, impacting prices and export volumes.
6. Challenges and Opportunities
- Infrastructure and Logistics: Challenges include the state of transport infrastructure, particularly the condition of roads and railways, which can affect the efficiency and cost of exporting.
- Policy Changes: The Zimbabwean government has been considering policies that might affect the export of raw chrome, including possible restrictions to encourage local value addition. Keeping up-to-date with these policies is essential for companies involved in the export of chrome concentrate.
- Environmental Concerns: Environmental regulations are becoming increasingly stringent, and companies must ensure they comply to avoid penalties or shutdowns.
7. Recent Developments
- Strategic Partnerships: The Zimbabwean government has been encouraging partnerships between local companies and foreign investors to boost production and improve the quality of chrome concentrate.
- Investment in Technology: There is an increasing focus on improving the efficiency of chrome concentration plants through the adoption of new technologies, which can enhance the quality of the final product and make Zimbabwean chrome more competitive in the global market.